Last year, Apple launched a program for processing old iPhones. As of today, robots dismantle them and remove the most valuable parts for further re-use. The rest is disposed with minimal harm to the environment. The concept of Industry 4.0 is often depicted as a mathematical sign of infinity – it illustrates this endless cycle of interaction between the manufacturer, the customer, and the product.
So what are the steps to implement such a scenario at enterprises? Four basic principles define the reality of Industry 4.0:
- The first is compatibility which means the ability of machines, devices, sensors and people to interact and communicate with each other via the Internet of things (IoT);
- This situation leads to the principle number two – the transparency that appears as a result of this interaction. In the virtual world, a digital copy of a real object or system of functions represents everything that happens to its physical clone. As a result, one may easily use the complete information about all processes that occur within “smart” products and production in general courtesy of the data from sensors. Obviously, one also should take into consideration the context in which the data is generated;
- Technical support is the third principle of Industry 4.0. Its essence lies in the fact that computer systems help people make decisions by collecting, analyzing and visualizing all the information mentioned above. Smart factories are capable of manufacturing data analysis of virtually any scope. This kind of support may also lead to the complete replacement of people with machines when performing dangerous or routine operations;
- The fourth principle is the decentralization of managerial decisions, with the further delegation of some of them to cyber-physical systems. The idea is that automation should be as complete as possible: if a machine can work effectively without human intervention, sooner or later a person’s replacement should occur. But it’s not something to be afraid of – it’s not about losing jobs, but creating new responsibilities for human employees. In the future, they will take the role of supervisors who can intervene in case of emergency or non-standard situations.
Eventually, as the result of the industry’s transition to these principles, there will be a change in business models. Instead of focusing on lean manufacturing, companies will try to introduce so-called “personalized mass products” on the principles of Agile and switch to a product line containing a ….single product. At the same time, the principle of saving is preserved: robotic production is more energy efficient, and it produces less waste and rejects.
Craving for Self-Expression
The transformation of the manufacturing industry is called a revolution precisely because changes are not superficial, but radical: the industry is being rebuilt from top to bottom. Business models are changing, new companies are born, and world famous brands with a long history are blown off the face of the earth if they do not have time to join the ranks of digital revolutionaries. Customers have changed their behavior, they want an individual approach, unique products, and no “consumer goods”. They no longer want to be the same, they try to emphasize their individual characteristics and express their mood.
Enterprises that are accustomed to producing the same things have to change their strategy. The introduction of the principles of Industry 4.0 allows you to get a number of advantages that are not available in traditional models of the past. For example, now companies can achieve an individual approach and personalize orders according to personal preferences of customers which dramatically increases their loyalty. Old factories and factories are becoming “smart” and begin to produce piece products on an individual order. At the same time costs per unit product are reduced, and companies are able to produce a unique personalized product at the cost of a mass standardized product.
For example, today you can enjoy your coffee in a cafe, download the Nike application or go to the company’s website, choose a model of sneakers, color them with the colors of your favorite football team, pay and receive it in a few weeks. It will cost $120 without shipping just like the usual non-personalized sneakers of the same company.
The manufacturer also has the opportunity to offer customers a large number of unique options for their product which provides an additional source of profit and increases the margin of the business. Basically, anything can be produced on an individual order. For instance, the Fujitsu factory in the German city of Augsburg produces computer systems and servers literally per piece for a specific customer.
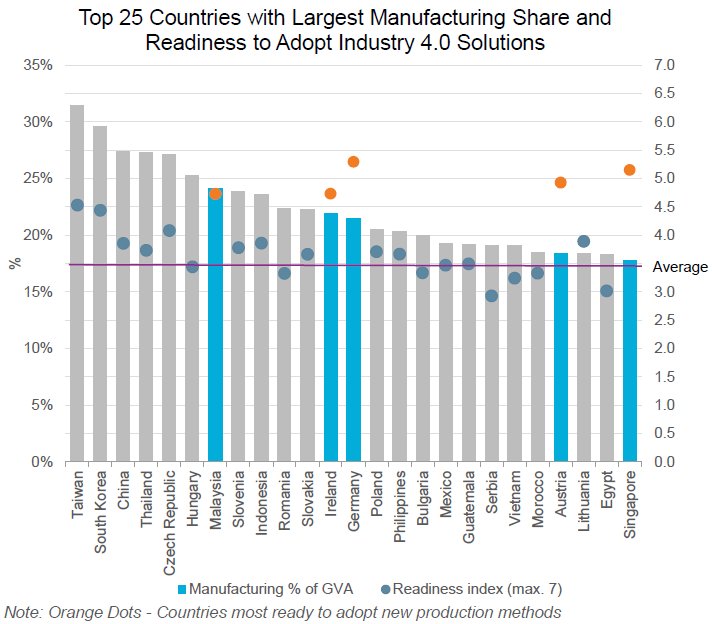
It’s worth noting that the expenses for the production of individual products for enterprise with deep automation are relatively small. In the past, one would have to reconfigure the equipment by hand for each pair of running shoes, today it is done in an instance by the computer system itself.
The other great example is the robotization of the Tesla electric vehicles factories. The automation of working processes allowed the company to expand production in California, not China. It turned out to be cheaper than employing Chinese workers and then paying for transportation of ready-made cars. Thanks to new technologies, another well-known manufacturer – Adidas – is moving its production back to Germany. At the new factory, all operations will be performed by robots. This new model optimizes production and, at the same time, dramatically increases its speed.
The Era of Change
However, it’s quite a difficult task to survive this wave of digital transformation. For instance, 52% of companies from the Fortune 500 rating (2000) do not exist today. But those who are able to restructure will benefit in a double way: current consumers who are loyal to respected brands will stay with them if they switch to an individual approach. For example, the shares of Harley-Davidson after the transformation of business in partnership with SAP (and through the introduction of the principles of Industry 4.0) have grown seven times in six years. Keep in mind the fact that the company experienced a serious drop in demand for its products due to the economic crisis. Now it’s possible to order a special model of the legendary Harley in your favorite colors and get it in six hours straight from the factory.
All these characteristics of new business models can lead to unpredictable changes in the world economy and highly dynamic transformation of the market. New technologies can have a devastating effect on legal issues (concerning, for example, important corporate data and their protection, liability, trade restrictions, etc.), so it is required to check the compliance of all developments to the law both before and during implementation. In addition, an equally important role in Industry 4.0 is the protection of network nodes and overall security – ensuring it only at the level of individual components will not be enough.