The integration of Extended Reality (XR) technologies, such as Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR), has been rapidly transforming various industries, including healthcare. The XR in healthcare market is projected to grow significantly by 2025, with applications such as virtual surgical simulation, patient education, and remote consultations driving adoption in regions, improving the quality of healthcare delivery.
The US healthcare market has been at the forefront of adopting XR in healthcare to improve patient care and medical training. According to a comprehensive report by Grand View Research, the US healthcare AR/VR market was valued at a remarkable $579.1 million in 2020, projected to catapult to a staggering $7.05 billion by 2028, boasting a commendable compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 35.2% during the period spanning 2021 to 2028.
Understanding XR in Healthcare: Core Concepts and Technology
The XR in healthcare market is rapidly expanding, projected to reach significant growth by 2025. XR medical applications, such as augmented reality (AR) for surgical simulations and virtual reality (VR) for patient education, are transforming the way healthcare is delivered. These technologies improve medical training, enhance patient outcomes, and facilitate remote consultations.
Regions such as North America and Europe are leading in adoption, driven by technological advancements and increased investment. As healthcare providers embrace XR healthcare solutions, patient engagement and care quality will continue to improve, paving the way for a more innovative future in medical practice.
Let’s establish the terminology of what we’re dealing with here.
Virtual Reality (VR) transports users into a complete digital setting using a headset or a surrounding display. This setting can be created by computers or captured through 360-degree video.
Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital information, objects, or media onto the real world using mobile devices or headsets. These elements can be displayed as graphical overlays or realistic 3D objects.
Mixed Reality (MR) represents the advanced form of AR, where physical and digital objects coexist harmoniously. In other words, digital objects appear integrated into and anchored to the real-world environment.
Immersive technology solutions, also known as XR (Extended Reality), are being implemented through diverse channels. Augmented reality experiences are commonly accessed via mobile phones or headsets, providing users with a visual overlay of digital objects within their surrounding environment. Conversely, virtual reality is utilized to fully immerse users within a digitally simulated environment, typically accomplished by employing a headset.
Top XR Medical Applications in Healthcare
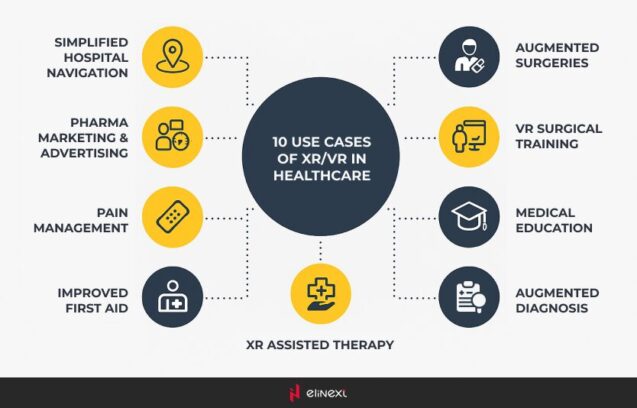
XR in healthcare is revolutionizing medical practices with various applications. Notable XR medical applications include surgical training simulations using augmented reality (AR), which allow surgeons to practice in a risk-free environment. Virtual reality (VR) is used for pain management and exposure therapy, helping patients cope with anxiety. Additionally, XR applications examples for patient education provide interactive experiences that enhance understanding of procedures and treatments. These innovations improve outcomes, streamline training, and foster better patient engagement in their healthcare journey.
Patient Care
mHealth app development services transform patient care by providing convenient access to health information and resources. These apps enable real-time communication between patients and providers, increasing engagement and adherence to treatment plans. Features such as appointment scheduling, medication reminders, and telehealth consultations enable patients to effectively manage their health, resulting in improved outcomes and satisfaction with the treatment experience.
Surgical Planning & Remote Collaboration
XR healthcare improves surgical planning and remote collaboration by providing immersive visualizations and simulations. Surgeons can use augmented reality (AR) to overlay critical data onto the surgical field, increasing accuracy during procedures. Virtual reality (VR) enables specialists to collaborate remotely, allowing them to discuss complex cases in real-time.
Rehabilitation & Physical Therapy
The immersive technology in healthcare market is having a significant impact on rehabilitation and physical therapy. Using virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), therapists can create engaging exercises that motivate patients during recovery. These technologies provide real-time feedback, allowing for the development of customized treatment plans that adapt to individual progress.
Mental Health & Pain Management
XR technology is becoming a powerful tool in addressing mental health and pain management. Virtual reality (VR) can help patients cope with chronic pain by providing an immersive environment that distracts from discomfort and reduces anxiety. This innovative approach allows for therapeutic interventions that promote relaxation and emotional resilience, ultimately improving recovery.
XR in Healthcare: Use Cases in Germany
Germany has been actively incorporating XR medical applications into various healthcare domains, showcasing the country’s commitment to innovation and patient care. Here are three notable examples of XR implementation in Germany:
XR in Surgical Training and Planning
The Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, one of Germany’s leading medical institutions, has been utilizing XR in surgical training and planning.
Here is how it works: surgeons can use VR to simulate complex surgical procedures, allowing them to practice and refine their techniques before operating on actual patients.
This technology provides a safe and controlled environment for surgeons to gain hands-on experience, enhance their skills, and reduce the risk of errors during real surgeries. Moreover, XR visualization tools assist in pre-operative planning by enabling surgeons to visualize patient-specific anatomy and simulate the surgical process, resulting in improved precision and outcomes.
XR for Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
XR technologies are also being harnessed for rehabilitation and physical therapy in Germany. The Rehawissenschaften Institute at the Technical University of Dortmund has been exploring the use of XR in neurorehabilitation. By combining virtual reality and motion-tracking devices, patients can engage in immersive and interactive rehabilitation exercises. These exercises help individuals regain motor functions, improve coordination, and enhance overall mobility. XR-based rehabilitation programs offer a motivating and engaging environment, increasing patient compliance and potentially expediting the recovery process.
XR for Mental Health Treatments
Germany addresses mental health conditions with the help of XR. For instance, the University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf has integrated XR technology into the treatment of anxiety disorders.
Patients suffering from phobias or anxiety can undergo exposure therapy in a virtual environment, gradually exposing themselves to their fears or triggers. XR applications examples allow therapists to create realistic scenarios that mimic real-life situations while providing a safe and controlled space for patients to confront their anxieties. These examples demonstrate Germany’s commitment to leveraging XR technologies to enhance medical training, rehabilitation, and mental health treatments. By embracing immersive technologies, Germany’s healthcare sector is paving the way for more personalized, effective, and patient-centric care.
Examples of Use in the US
XR in Pain Management
The Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in LA, has been utilizing XR technology to help manage acute and chronic pain.
By immersing patients in virtual environments, XR experiences can distract them from their pain and promote relaxation. Additionally, XR can be combined with biofeedback techniques to provide real-time physiological data, enabling patients to visualize and regulate their pain responses. This approach offers a non-pharmacological method for pain management and has shown promising results in reducing pain levels and improving patients’ overall well-being.
XR in Medical Education
Medical institutions in the United States, such as Stanford University School of Medicine, have embraced XR technologies to enhance medical education. Virtual reality simulations allow students to practice medical procedures, interact with virtual patients, and develop clinical skills in a safe and controlled environment.
XR provides an immersive and engaging learning experience, enabling students to gain practical knowledge and improve their decision-making abilities. By integrating immersive technology in healthcare market, educational institutions are preparing future healthcare professionals for real-world scenarios more effectively. Those are just a few examples of XR applications across these gigantic markets, as all the 20 clinical sectors mentioned before were involved.
The Future of XR in the Global Healthcare Market
The AR/VR market in healthcare is poised for significant growth as demand for innovative solutions accelerates. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of XR technologies, pushing healthcare providers towards digital transformation. Healthcare software development services are evolving to integrate AR and VR, improving training, patient engagement, and treatment outcomes. As immersive technologies mature, they will revolutionize diagnostics and therapy, offering personalized experiences that improve patient care. The future of XR in healthcare promises to improve efficiency, accessibility, and equity in healthcare services worldwide.
Conclusion
The United States and Germany have emerged as frontrunners in adopting XR technologies in healthcare. The great numbers reflect the increasing recognition and investment in XR technologies within the healthcare industry.
Healthcare AR/VR market offers a wide range of applications in healthcare, including surgical training and planning, rehabilitation and physical therapy, mental health treatments, pain management, medical education, and more. The immersive and interactive nature of XR experiences provides a safe and controlled environment for medical professionals and patients to enhance their skills, promote recovery, and address various medical conditions.
The accessibility and cost-effectiveness improvements in XR technology have facilitated its rapid progress and adoption across the healthcare sector. Furthermore, advancements in related technologies such as 5G, AI, IoT, and machine learning have contributed to the increased trust and reliability of immersive experiences. As XR technology continues to evolve, we can expect further advancements and applications in healthcare. If you’re looking for an experienced XR software developer in the healthcare domain, contact Elinext, and we’ll pursue your interests in entering the market together.
FAQ
How is immersive technology used in the healthcare market?
Immersive technology such as VR and AR are used in healthcare for training simulations, patient education, pain management, and rehabilitation. These technologies increase engagement, improve outcomes, and provide a safe environment for practice.
What are the benefits of XR in healthcare?
AR/VR app development services improve healthcare by enhancing education, increasing patient engagement, and offering effective pain management solutions. XR facilitates personalized care, reduces anxiety, and supports rehabilitation efforts.
Is XR technology already widely adopted in hospitals?
XR technology is gaining traction in hospitals, but its adoption is not yet widespread. Many facilities are exploring its potential for training, patient treatment, and pain management, gradually integrating these solutions.