From “Wearable Cyborg” to AI-driven solutions for early disease detection, this article highlights health tech that is changing healthcare in Japan.
Japan’s impressive technological advancements have long attracted worldwide attention. Be it the world’s first commercial camera phone or Android robots, Japan has been a home for some of the best tech inventions in history.
However, the last decade has witnessed Japanese tech firms placing a strong emphasis on advancing developments in medical technologies.
High life expectancy and critically low birth rates have contributed to making the country a global leader in aging societies. The aging Japanese population increases the strain on already overworked nursing staff, pushing leading local innovators to find solutions to lack of staff, inaccessibility to proper care, and rising healthcare costs through custom healthcare app development.
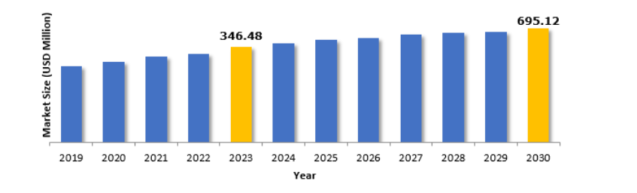
Based on recent estimates by BlueWeave Consulting, the Japan HealthTech Market is expected to experience a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.16% between 2024 and 2030.
Source: BlueWeave Consulting
No silver bullet can completely solve the country’s healthcare crisis, but these technological advancements, however, are able to help address staffing shortages and burnout as well as boost patient outcomes.
Robotics
In Japan, robots are often seen as a natural solution to the challenges of caring for the elderly and the disabled.
The country boasts extensive expertise in industrial robotics and has been a pioneer in humanoid robot research for several decades.
Japanese healthcare robots come in all stripes, each serving specific purposes. Some machines are designed to help the elderly and users with reduced mobility in physical activities of daily living. They lift patients out of their beds and wheelchairs and transfer them to new positions, monitor physical activity and promptly detect falls, provide feeding assistance, help with hygiene chores, etc. (Robear, RIBA).
Others are meant for care for older adults with mild cognitive decline. They can help manage dementia-related conditions by providing reminders, assisting with daily routines, and reducing caregiver burden.
Conversation robots might also engage older people through interactive activities, games, and memory exercises. These “talking machines” have a positive impact on loneliness severity among users by providing emotional support, conversation, and a sense of connection. ( Pepper, Paro, Aibo).
Leading Japanese robotics companies also focused on the extensive development of robotic prosthetics and exoskeletons. These advanced devices are specifically designed to aid individuals with limb loss or mobility impairments, empowering them to reclaim their independence.
A striking example is Cyberdyne’s HAL — or Hybrid Assistive Limb — the world’s first wearable robotic suit. “Wearable Cyborg” supports, enhances and regenerates the wearer’s physical functions based on their intentions.
Cyberdyne claims that this technology can magnify a person’s strength by a factor of 10.
Remote Health Services
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, original guidelines requiring doctors to examine patients in person before being able to order prescriptions have shifted in Japan. Telemedicine, which encompasses online consultations, cloud-based medical records, and remote patient monitoring, is now gaining momentum.
One clear illustration of this is a Wellness Hub, a smart system developed by Acer in collaboration with Allxon (a startup spun off from Acer) and Japanese health authorities to enhance remote healthcare services for elderly patients in Japan.
Non-intrusive solution enables caregivers and medical staff to collect and monitor a patient’s health data such as blood glucose levels and blood pressure with the help of LTE and Bluetooth devices. That eliminates the need for in-person visits, which can be time-consuming and costly, especially in rural areas.
Omron and Port are also contributing significantly to bridging the gap between medical professionals and patients with their advanced telemedicine platforms and devices.
Intelligent Wearables
Wearable technology is experiencing rapid growth in Japan as it offers unparalleled convenience and allows users to live healthier and more connected lives.
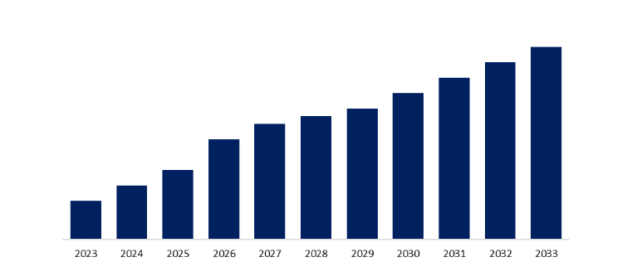
The Japan Wearable Technology Market is projected to grow substantially, with a CAGR of 15.03% from 2023 to 2033.
Source: Spherical Insights
One noteworthy development in the field of wearables is DFree (by Triple W Japan Inc.,) — the world’s first connected wearable device that can monitor the change of bladder size using non-invasive ultrasonic sensors and notify users through the mobile app of the need to use the toilet.
This innovative solution helps elderly and disabled individuals who suffer from incontinence live without diapers and alleviates stress and embarrassment associated with incontinence. Today, DFree’s award-winning technology is used in over 500 nursing and care homes in Japan, America, and Europe.
Xenoma’s wearable e-skin MEVA is another groundbreaking wearable technology designed by Japanese engineers with the needs of older people in mind.
The smart clothing assesses skin temperature, respiration, motion and posture, and works both while the wearer is awake and asleep.
MEVA incorporates advanced fall detection technology that can distinguish between types of falls and sends an immediate alert to emergency contacts or healthcare providers if necessary.
AI-Driven Solutions For Early Disease Detection
According to the World Health Organization, cancer is among the leading causes of death globally.
In Japan, AI became one of the major resources put into this area to improve early detection.
A great example is the recent achievement of AIM, a Tokyo-based medtech company specializing in the development of diagnostic endoscopic AI. The medical start-up has created an AI-based endoscopic diagnostic support system that is capable of identifying early-stage gastric cancer, a disease diagnosed in around 26,000 people in America every year.
Trained with over 200,000 high-resolution videos from medical institutions across Japan, this AI can quickly assess still images and videos in real time.
It assists physicians by identifying suspicious areas during endoscopic examinations, potentially reducing missed early-stage stomach cancers. The tool analyzes a single image in just 0.02 seconds, much faster than specialist physicians’ typical four seconds.
Healthcare Technology for Surgery
Although we already mentioned awesome Japanese robotics innovations at the beginning of our article, the way these smart machines are used within the operating room is absolutely fascinating and deserves a separate description.
In Japan, robotic surgical assistants vary widely in form and size, ranging from the miniature device that crawls the surface of the heart to a massive arm that acts as another pair of hands during complex procedures.
Our particular attention is drawn to the “hinotori Surgical Robot System” — Japanese first ever robotic-assisted surgery system.
Initially approved by Japanese regulatory authorities for urology, its application has since expanded to include gastroenterology, gynecology, and respiratory surgery.
The hinotori system is built with a focus on compactness, safety, and high maneuverability.
The surgeon operates the instruments and 3D endoscope camera using the hands and feet. A surgeon’s cockpit is ergonomically designed to reduce fatigue during operations. This helps perform complex surgeries with greater precision and accuracy.
Since its launch in December 2020, the hinotori system has been used in over 2,000 cases across various medical institutions.
Medical robots aren’t the only tech to invade the field of surgery in Japan, though. Virtual and augmented reality also assist doctors in surgical practices and patient care. For instance, the VR solution created by Holoeyes is winning over medical professionals all over Japan, changing the way surgery is done.
The team behind Holoeyes uses CT scans to build up a virtual reality model of patients’ organs, which surgeons can examine in detail.
Do You Need Help With Building Breakthrough Healthcare Technology? The Elinext Team Is Here To Assist You Every Step Of The Way.
Elinext is a premier full-service custom software development company with a team of more than 700 dedicated software developers specializing in architecting scalable custom software solutions in Healthcare, Banking, Data Analytics, ERP and Asset Management, CRM and Loyalty, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Blockchain, Cybersecurity, IoT, and IT Infrastructure Management domains.
As a tech partner with 27+ years of industry expertise, we have a good store of knowledge, making us fully prepared to help hospitals, pharmacies, labs, and other healthcare players with their projects, regardless of the complexity, tech limitations, or regulatory hurdles.
Examples of our successful projects across the healthcare sector include a Healthcare Data Anonymization Platform, Software For Cardiovascular Care Providers, a Platform For Mental Health Counselling In Canada, and a Mobile Fitness Application For The Australian Market.
One of our exciting cases, developing Medical Practice And Billing Software, stands out particularly.
The HIPAA-compliant system not only allows management of medical records, billing, and payments, but also makes it possible for patients and doctors to buy medicaments within the app, reach out to coaches, staff, vendors, and billing team, and even create customized documents and application forms with unique styles.
Have a look at our Case Studies page for some more examples of how we’ve helped companies with the implementation of their business idea and get in touch here to see if we could be a match.