IoT + Medical devices = IoMT?
This equation is already shaking the grounds of healthcare by using the Internet to connect medical devices, healthcare professionals, and patients in real time. The outcome is not difficult to guess: improved healthcare quality on multiple layers and big business – already ripe for innovation – for key market players. From lower costs to improved patient comfort, enhanced diagnosis accuracy, or personalized treatments, IoMT represents a major shift toward value-driven, patient-centred, and preventive healthcare services.
IoMT- What is it exactly?
IoMT (i.e. The Internet of Medical Things) can be defined in terms of an Internet-connected network – encompassing hardware, software, and medical devices – thought out to enable the fast analysis of medical data. In layman’s terms, IoMT is all about smart medical devices able to transfer patient data via the Internet.
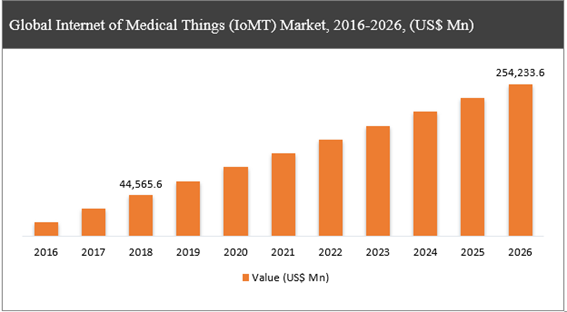
According to All The Research, by 2026, the IoMT market is expected to reach USD 254,233.6 million, growing at a CAGR of 24.4%.
Influenced by various determining factors – such as the restrictions during the COVID-19 pandemic, the aging population, the growing demand for personalised and precise care, increased accessibility of sensor technology, or the high rates of chronic diseases, – the healthcare system is already undergoing a technological metamorphosis that is not expected to slow down in the upcoming years.
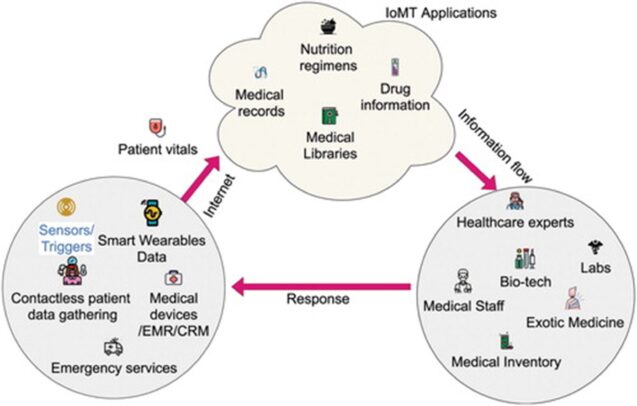
Before we get to take a look at some widely used solutions and novel technologies, it is important to understand how IoMT actually works. In their article Internet of Medical Things (IoMT): Overview, Emerging Technologies, and Case Studies, Sahshanu Razdan and Sachin Sharma use the following figure to exemplify how information collected by means of sensor devices flows from the patient to the IoMT apps, healthcare experts, and back to the patient.
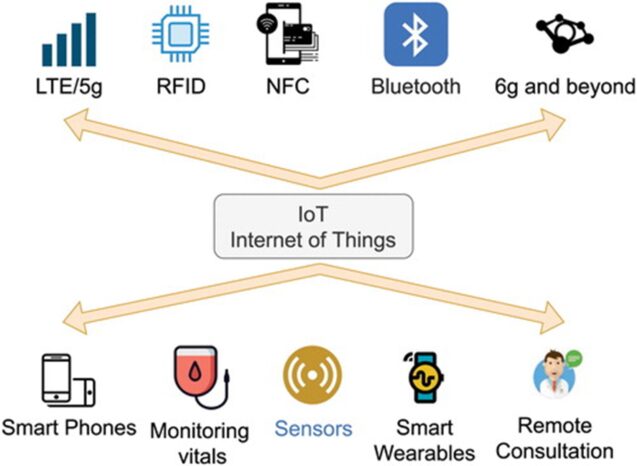
The same article also offers relevant examples of wireless technologies and medical devices that are forever changing healthcare as we used to know it:
Put simply: medical digital devices collect, analyse, and send data in real-time via wireless technologies (e.g. 5G/6G, Zigbee, Power Line Communication (PLC), Ethernet, LoRaWAN, etc.) which offer crucial benefits such as low latency, high bandwidth, coverage, etc. It becomes obvious that, in order to work seamlessly, IoMT heavily relies not only on advanced medical devices but also on IoT connectivity and healthcare IT systems. Is there room for AI and ML in this equation? Since healthcare professionals may be overwhelmed with vast amounts of collected data, AI may ease their burden and provide only relevant data. Could ML revolutionize, for instance, mental health monitoring? We will talk about AI, ML, and NLP at a later point in this article. In the meantime, let’s take a look at some relevant solutions that are already widely used:
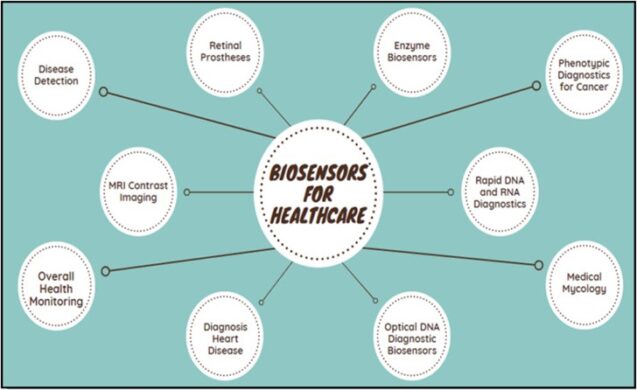
Medical sensors
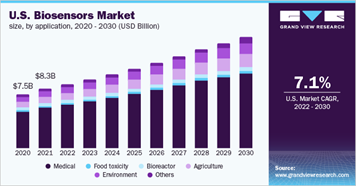
With biosensors already dominating the medical field and projected to become key components in a wide array of industries (e.g. food industry, imaging, agriculture, etc.), there is no wonder that, in 2021, the value of the global biosensors market reached USD 24.9 billion. According to Grand View Research, from 2022 to 2030, the global biosensors market will keep expanding at a CAGR of 8.0%.
With the first oxygen biosensor being developed back in 1962, it is clear that biosensors are no novelty. However, over the years, the capabilities and applications of biosensors – especially in healthcare – have come a long, long way.
Source: Sciencedirect
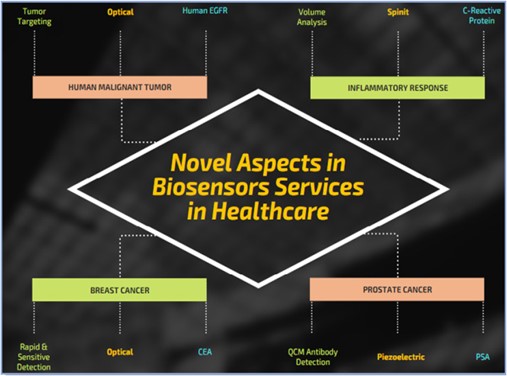
As the authors of Biosensors applications in medical field: A brief review point out, biosensors are already revolutionizing cancer detection and monitoring:
The application of biosensors in healthcare already goes well beyond monitoring the patient’s heart rate, temperature, blood sugar level, hydration, or sweat. For instance, biosensors are expected to support ‘the creation of personalised cancer therapy by measuring quick, highly localised, and transitory changes in tumour response to radiation therapy and chemotherapy’ (Haleem, Abid, et al., 2021.)
Software solutions
Collecting vast amounts of medical data would be nothing but a waste of time without an accurate, secure, and reliable app to make it visible, consistent, and accessible. The offer is so varied that it would be virtually impossible to list all the available solutions. Let’s take a look at some of the most common ones:
- Telehealth and telemedicine software
- Apps for monitoring chronic diseases
- Hospital infrastructure management
- Medication reminders
- Software for data visualization and analysis
- Medical CRMs
- Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
- E-prescriptions software
- Diagnosis apps for healthcare professionals and patients
AI in healthcare
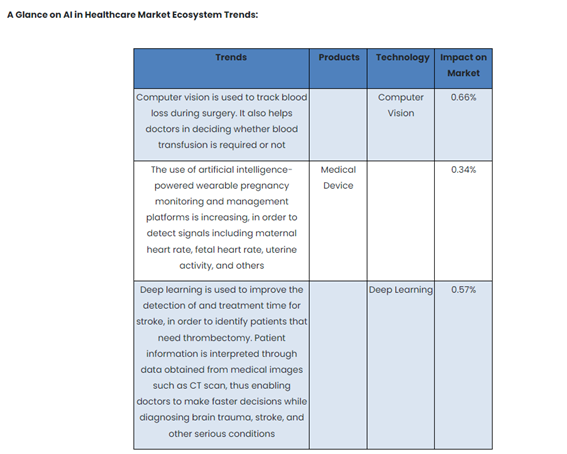
In a report published in July 2020, All The Research estimates that, by 2027, AI in healthcare market size will reach $ 30.9 Bn, growing at a CAGR of 24%. According to the same source, this is how AI projects itself in the Healthcare Market Ecosystem:
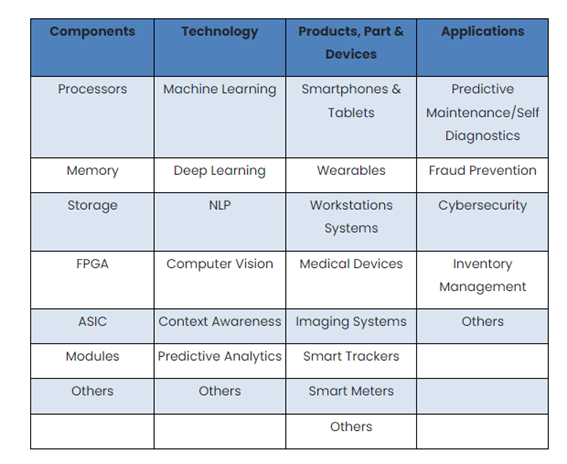 As pointed out in A review of enabling technologies for Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Ecosystem, ML and AI techniques can be used to monitor patients’ emotional health and stress levels, making it possible to predict potential mental disorders and illnesses. Even though there are various available models (e.g. GSR-Galvanic Skin Response, PPG signals, etc.), research in the mental health field is still in its incipient phases. Even though in an experimental stage, various models based on state-of-the-art machine learning classification algorithms are being developed to prevent and detect falls in the elderly. (Ashfaq, Zarlish, et al., 2022.)
As pointed out in A review of enabling technologies for Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Ecosystem, ML and AI techniques can be used to monitor patients’ emotional health and stress levels, making it possible to predict potential mental disorders and illnesses. Even though there are various available models (e.g. GSR-Galvanic Skin Response, PPG signals, etc.), research in the mental health field is still in its incipient phases. Even though in an experimental stage, various models based on state-of-the-art machine learning classification algorithms are being developed to prevent and detect falls in the elderly. (Ashfaq, Zarlish, et al., 2022.)
All The Research distinguishes three other trends in the use of AI in healthcare:
Will technological innovation continue to reconfigure the healthcare landscape? Undoubtedly, YES. To what extent? We are yet to see. What becomes clear is that IoMT provides a series of major advantages:
- Improved patient outcomes: since healthcare professionals have access to real-time, accurate patient data, they are able to make error-free, well-informed decisions. Being able to remotely monitor patients who suffer from chronic diseases has substantially reduced the need for in-person visits.
- Disease prevention: since IoMT is oriented toward disease prevention and remote patient monitoring, it helps reduce readmissions, hospital stays, or in-person visits. And that translates into lower costs.
- Enhanced patient engagement: as consumer-grade wearables (e.g. smart watches, activity, trackers, etc.) have become more and more accessible, many patients are nowadays actively monitoring their own health.
- Improved access to healthcare services: IoMT has made it possible for isolated patients (due to geographical reasons, physical constraints, or whatever other reasons that prevent them from travelling) to have access to quality healthcare services via technologies such as clinical-grade wearables or telehealth appointments.
- Easy implementation: IoMT devices have been thought out to be easy to implement and use, allowing patients to monitor their vitals in real-time.
Wrap up
While it is true that healthcare is a complex and highly-sensitive industry and its digitalization is far from being a challenge-free process, IoMT solutions represent an adrenaline shot meant to improve patient outcomes and overall experience, reduce costs, and reduce the burden on healthcare professionals. Despite the existing challenges (i.e. security and privacy concerns, regulatory and legal inconsistencies, technical challenges, etc.), we wouldn’t be far from the truth to conclude that IoMT technologies are slowly turning the prescriptive healthcare model we are all used to into a preventive one that will allow us all to live longer and healthier lives.