Even before the pandemic hit, the health insurance industry was struggling with growth and profitability in a low-interest-rate environment and toughening regulations. Now that COVID-19 is raging on, insurers are caught between a rock and a hard place, trying to protect their profit margins while supporting their customers through the crisis.
To cope with these challenges, health and life insurers are increasingly turning to technology — namely, big data. The ever-increasing volumes of medical big data and rapidly improving analytical capabilities empower healthcare providers and insurers with deep insights that translate into a range of advantages, from personalized insurance policies to automated fraud detection.
But before we dive into the benefits of data-driven healthcare solutions for better health insurance, let’s see what sources of medical big data there are.
Sources of medical big data
Traditionally, life and health insurers collected personal information during a patient onboarding in order to improve customer service. But the technology evolves in leaps and bounds, opening new data goldmines for insurers to tap into.
- Internet of Things solutions including wearables, connected sensors, and devices that enable smart, real-time patient monitoring
- mHealth applications that track a person’s exercise and sleep regime, medication intake, and other health-related activities
- Medical images including X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs
- EHR and EMR systems that provide a holistic picture of a patient’s health
- Clinical trials, research studies, and screening libraries
- Health insurance claims and medical billing
- Genomics and other omics disciplines (transcriptomics, proteomics, epigenomic, metagenomics, metabolomics, nutriomics, etc.)
- Biotechnology including medical-grade embedded devices
Sitting on this insurmountable amount of data, insurers are still often known as being data-rich, but information-poor. But by investing in custom healthcare analytics solutions, insurance providers stand to benefit in a big way.
Personalized health insurance plans
Whether it’s a treatment plan or health coverage, patients want their personal needs to be taken into account. And big data analytics helps insurers do just that. With the abundance of patient data from wearables, sensors, mobile apps, and even implantable medical devices, health insurers can get a 360-degree view of a patient and craft customized health plans, delivering the right coverage to the right person.
What’s more, real-time data collected from wearables allow health and life insurers to gain a better understanding of a patient’s lifestyle. Insurers can further leverage the additional insights to encourage better habits among the insureds and award them with lower premiums and other benefits.
Improved medical underwriting
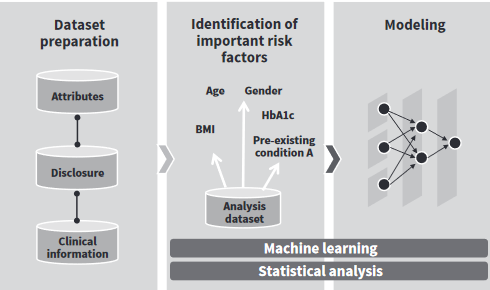
In health insurance, underwriting decisions are based on the information provided by an applicant and on the results of an applicant’s health check, also known as risk assessment. This risk evaluation process is crucial to effective medical underwriting as accepting a large number of high-risk candidates can undermine the viability of an insurance system.
But more often than not, risk assessment is grounded on best-practice estimates and general guidelines. By leveraging big data analytics, insurers can build sophisticated predictive models to make the acceptance criteria more fine-grained and streamline medical underwriting. These ML-driven models quickly and easily digest medical information from insurance applications, clinical registries, claims, third-party databases, and other sources, saving time and minimizing human error.
Source: Hitachi Review
Increased price transparency
The pressure around insurance price transparency is increasing. The newly finalized rule, released by Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), requires insurers to share prices for healthcare services and patient cost-sharing with the public. Starting in 2023, insurers must offer an online shopping tool that will help consumers see an estimate of their out-of-pocket cost for 500 of the most shoppable services.
But with countless providers, a growing number of products, and large health data sets, the healthcare ecosystem is complex and highly variable. Big data analytics can turn out to be a powerful ally in the battle for improving price information accessibility. Powered by machine learning, healthcare analytics solutions can marry pricing data and outcome metrics to help patients find the highest value, lowest cost provider and make an informed decision.
Accurate fraud detection
Health insurance fraud is a multi-billion dollar problem. In the US alone, healthcare fraud costs the nation about $68 billion every year, inevitably translating into higher premiums, reduced coverage benefits, and other out-of-pocket expenses. And with the global efforts to reduce healthcare costs, timely insurance fraud detection becomes of paramount importance.
Just like fintech startups are using big data analytics to detect suspicious activity and immediately block a credit card, so these capabilities can be leveraged to identify health insurance fraud almost in real-time.
Advanced data-driven algorithms allow insurers to quickly process both structured and unstructured data to build a predictive model that would identify erroneous or suspicious claims in a matter of seconds. These data-driven models analyze the behavior of a specific customer and the particular use case to accurately detect a fraudulent activity and compute the likelihood of an invalid claim.
Summing up
With the increasing healthcare digitization and adoption of mHealth and wearable technologies, the volume of big data is growing exponentially, reaching a whopping 2,314 exabytes in 2020.
Thanks to the advancements in big data analytics, these are not merely data sets but a harbor of deep, actionable insights that help insurers improve their operational efficiencies and take a step towards a customer-centric insurance model. From personalized health insurance to streamlined medical underwriting to real-time fraud detection, medical big data enables service providers to drive better, value-based insurance.