“The art of taxation consists in so plucking the goose as to get the most feathers with the least hissing.”
Jean Baptist Colbert
Digitalization has infused our lives in each and every facet. And no government can exist without taxation. Can these statements mingle to take Colbert’s metaphor to a whole new level of innovation? In a preponderantly tech-powered world that is gaining even further momentum in the post-COVID era, tax digitalization looks like a sensible path to take. To keep up with an ever-evolving and challenging financial environment, tax departments have become the lynchpin of the governmental jigsaw, allowing taxpayers to respond accordingly to the increased pressure imposed by regulators and the general public. As highlighted by 360 ResearchReports, the Tax Technology market is forecasted to reach $30471.82 million by 2027, thus responding to a pressing need for tax streamlining and transparency. From taxpayers – either businesses or ordinary citizens – to tax administrations, tax digitalization is nothing but an inevitable response to technological advancements.
Digital Tax Administration Transformation: an overview
According to 360 ResearchReports, in 2021, the global size of the Digital Transformation in Tax Technology market registered $13367.91 million and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.72%, reaching $30471.82 million by 2027.
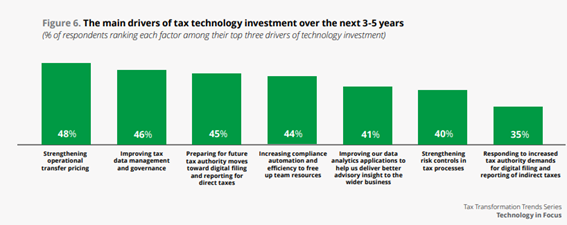
According to a survey published in April 2022 by Deloitte, in a global ecosystem that places its bets on transparency, investing in their tax departments will allow businesses to adequately respond to the increased public and taxing authorities pressure. There are multiple factors that fuel the digital tax transformation:
With regulators flipping the coin to digital tax administration, 75% of the respondents consider that, in the near future, tax authorities will directly access their IT systems:

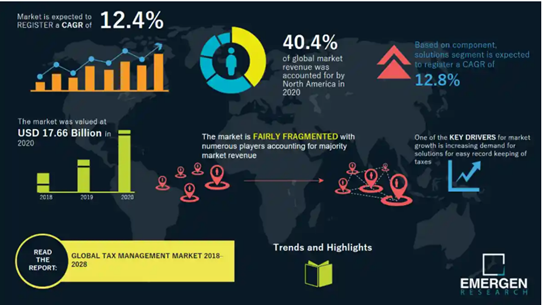
According to Emergen Research, the pressing need to avoid inconsistencies and automate taxation, thus streamlining processes, will fuel market growth even further:
Benefits of tax digitalization
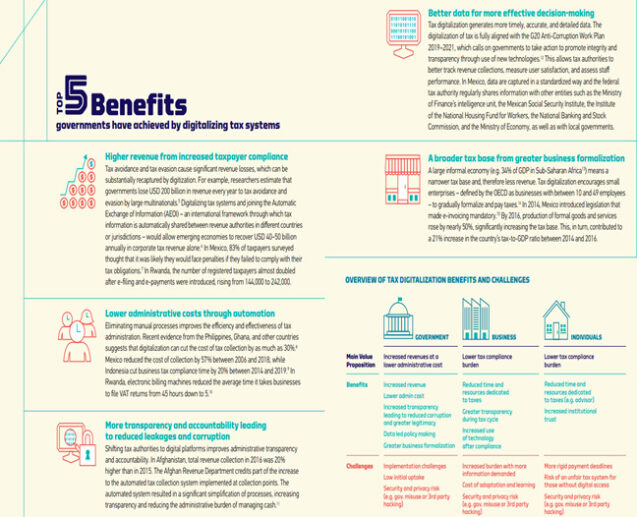
World Bank highlights several reasons why tax administrations are embracing digital transformation:
- Simplifies and facilitates compliance, reducing the administrative burden
- Appropriate taxation of the digital economy (e-commerce, cashless payments, etc.)
- Allows for information cross-checking and real-time tax information gathering, thus enhancing compliance
- AI-powered systems allow administrations to make better predictions
- Improved data-driven decision-making
- Reduced administrative costs and improved controls
- Improved communication with taxpayers, thus enhancing their trust
Taxpayers also benefit from digital transformation:
- Reduced tax errors
- Timely and straightforward tax payments
- Eliminates tedious paperwork
- Reduction of human intervention
- Easier bookkeeping
- Improved control of incomings and outgoings
The Success Factors in Tax Digitalization guide summarizes the benefits and challenges:
Digital Tax Administration Transformation in Germany
In an attempt to streamline and improve tax collection processes, Germany has been betting hard for digitalization and implemented a series of digital tax initiatives such as ELSTER (Elektronische Steuererklärung), the electronic tax filing system that allows both businesses and individuals to easily and securely submit their tax returns and declarations using finance software provided by the Federal Central Tax Office (BZSt), thus minimizing errors and substantially reducing the processing time. The ELSTER system is supported by third-party providers who develop software able to interact with the system. The system not only supports electronic communications between authorities and taxpayers but also facilitates the exchange of sensitive data between tax authorities and other governmental agencies. In a nutshell, with a centralized tax system and a central data exchange platform, taxpayers and authorities can share information electronically, thus enabling more accurate and faster data processing and drastically reducing the need for manual data entry.
In 2020, Germany implemented E-Invoicing-Verordnung, an electronic invoice that requires businesses to issue digital invoices in a standardized format. The system not only reduces paperwork and streamlines tax processes but also helps prevent fraud.
After the OECD published the guidelines for tax risk management procedures in 2016, the German Institute of Public Auditors Germany adopted IDW PS 980, a real-time tax compliance monitoring system that allows tax authorities to identify tax evasion risks. As a result, the system helps to increase transparency and ensure legal and regulatory compliance.
Digital Tax Administration Transformation in Austria
Similar to Germany, the Austrian Federal Ministry of Finance implemented FinanzOnline, a tax administration online portal that allows both businesses and individuals to securely make electronic payments, file tax returns, view tax records and request certificates, or communicate with tax authorities. Even though FinanzOnline was implemented in 2003, the system has been subject to continuous upgrades and currently features an interactive assistant for tax assessment.
In order to reduce paperwork, save costs, and enhance efficiency, Austria implemented e-Rechnung, an electronic invoicing system that businesses use to issue e-invoices to public authorities. To propel the adoption of electronic invoicing (e.g. Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), web-based portals, etc.), the Austrian government grants businesses tax incentives and subsidies.
The implementation of Registrierkassen (i.e. software and/or hardware that automatically records financial transactions in real-time) not only allows tax authorities to prevent fraud and tax evasion but also allows businesses to automate and track sales processes and transactions.
Digital Tax Administration Transformation in Switzerland
In its commitment to optimizing tax processes, the Swiss authorities implemented TaxMe, an online portal that allows taxpayers to file tax returns electronically. The system provides guidance to ensure that forms are filled correctly and taxpayers claim all the deductions they are eligible for. To make it even easier for taxpayers to manage tax processes, the Swiss Federal Tax Administration implemented eTax, an online platform that allows registered users to file tax returns, access their tax history and current status, and make payments via the e-banking services provided by the system. The system provides notifications for tax due dates, payment confirmation, and tax assessments. To enhance its utility and effectiveness, the system sends notifications for tax assessments and due dates, as well as payment confirmations.
As a result of its commitment to financial transparency, Switzerland has signed multiple international agreements that facilitate the exchange of tax information between countries. One of the most notable ones is the Automatic Exchange of Information (AEOI), an international agreement developed by OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development). Thought out to prevent tax evasion and ensure transparency by ensuring the cooperation between countries, the agreement requires financial institutions to report information (e.g. income, transactions, bank account balances, etc.) on foreign account holders to their national tax authority. To ensure the security, accuracy, and functionality of the data exchange process, the system makes use of a wide variety of advanced technologies such as CRS (Common Reporting Standard), secure data transfer protocols (e.g. SFTP), data management systems, encryption and decryption tools, or ML and advanced analytics to identify patterns and inconsistencies that may indicate tax evasion or other suspicious activities such as money laundering.
Wrap up
Up until not long ago, the relationship between taxpayers and tax administrations could be summarized in two words: time-consuming and challenging. “Today, it takes more brains and effort to make out the income-tax form than it does to make the income,” used to say Alfred E. Neuman wittily. However, initiatives such as ELSTER, Registrierkassen, TaxMe, or IDW PS 980 demonstrate that technology can streamline tax processes and make taxpayers’ lives a lot easier. Even though the shift toward tax digitalization can be hefty, the benefits for all the involved parties – tax authorities, taxpayers, and governments – are noteworthy: simplification, agility, bureaucracy reduction, cost reduction, and enhanced transparency. With a representative office in Berlin, Germany, Elinext builds customized tax software solutions for fast and accurate results.