This article aims to provide a detailed understanding of DEX liquidity. We will walk through its importance, and explore its mechanisms, the influencing factors, as well as strategies for boosting liquidity on DEX exchanges.
Since 2012 when the first rudimentary decentralized exchanges were launched, DEXs have grown increasingly prominent in the decentralized finance landscape.
By enabling users to engage in a fully permissionless and peer-to-peer manner, exchanges like Uniswap and PancakeSwap have revolutionized the way cryptocurrencies are traded and continue making waves in the world of DeFi.
According to recent data from DeFiLlama, a DeFi TVL (total value locked) aggregator, DEXs collectively handle around $6 billion in daily trading volume and roughly $45 billion weekly, led by platforms such as Raydium and Uniswap on Solana.
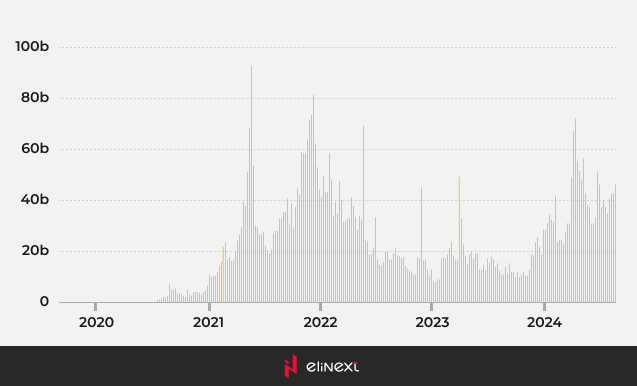
Weekly DEX volume, as of July 2024
Source: DefiLlama
Understanding DEX Liquidity Pools
Liquidity in crypto — the ability to buy or sell an asset easily or efficiently at a fair price — is pivotal for any exchange, whether it’s decentralized or not.
Liquidity is a key consideration for crypto traders and investors for a couple of reasons:
- Price Discovery and Stability: Liquidity promotes efficient price discovery, ensuring that asset prices accurately reflect their true market value based on supply and demand dynamics. This stability draws more participants, fostering a virtuous cycle of growing liquidity.
- Lower Trading Costs: In markets with high liquidity, the difference between the bid and ask prices is typically smaller, leading to lower transaction costs.
- More Effective Trading: In liquid markets, traders can more easily enter and exit positions, minimizing the risk of slippage — the difference between expected and actual trade prices.
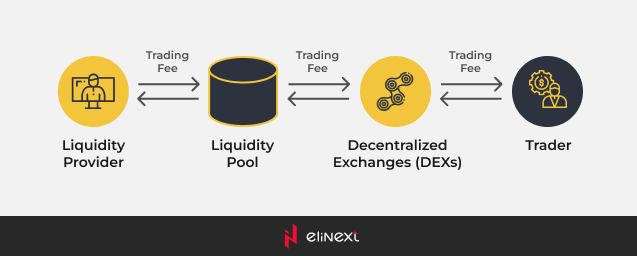
Liquidity pools are a mechanism that lets users pool their assets in a DEX’s smart contracts, thus providing much-needed asset liquidity and convenience for traders.
The emergence of liquidity pools has led some of the major decentralized exchanges to grow their liquidity bases to the extent that they even surpassed some of the early centralized cryptocurrency exchanges.
Some key drivers behind the rising number of investors (or liquidity providers) willing to deposit their assets to these pools are the promise of receiving a share of the exchange’s trading fees and such investment incentives as, for example, the distribution of the protocol’s native tokens.
The advent of liquidity pools became the answer to the liquidity problem that plagued the first versions of decentralized exchanges like Bancor.
How Exactly DEX Liquidity Pools Work
Liquidity pools give crypto traders the ability to buy and sell tokens on a DEX without the need to rely on a traditional centralized order book. Instead, a smart contract that controls the pool is responsible for continuous and automated trading.
Automated market maker (AMM) algorithms in the contract determine the price of assets based on the ratio of assets in the pool.
Source: Horizen Academy
Liquidity Pool Tokens (LPTs)
Liquidity pool tokens are digital assets issued to liquidity providers when they add their assets to the liquidity pool. Essentially, they serve as a kind of receipt representing the liquidity providers’ share of the pool.
Owning LPTs gives the investor a portion of the transaction fees generated by the pool’s activities, as well as any additional rewards offered by the DeFi platform.
The amount of owned LP tokens corresponds to the liquidity share the investor provided.
Providers can redeem their LP tokens from the liquidity pools along with the interest earned at any time.
DEX vs. CEX: Comparing Liquidity, Security, Speed And More
Which is better: DEX or CEX? Choosing between the methods shapes our trading experience, so the question is always relevant in the crypto community.
The answer to the DEX vs. CEX debate is neither is inherently better. The choice is a matter of personal needs, priorities, and goals.
Below is the comparison table highlighting DEX and CEX differences in depth.
CEX vs. DEX: A Thorough Comparison
| Feature | CEX | DEX |
| Operator | Centralized intermediaries | Smart contracts. Transactions occur directly between users. |
| Access | Participants need to create accounts. | Users need to connect their cryptocurrency wallet to begin trading. |
| Censorship Resistance | The centralized entity has the right to disable crypto trading and account closures. | DEXs operate in a legal gray area as regulations continue to develop. DEXs are less susceptible to censorship or government intervention. |
| Privacy | Users are required to complete KYC procedures to use a CEX. | There is no need to submit personal information. |
| User Interface | User-friendly interfaces designed for beginners. | Complex interfaces that require a deep understanding of blockchain technology. |
| Liquidity Sources | Provided by the centralized companies and market makers. | DEX liquidity pools. |
| Level of Liquidity | Generally have higher liquidity due to their established market presence and larger user bases. | May experience lower liquidity for less popular tokens, which can result in potential price fluctuations.
Most popular tokens like ETH and BTC typically have sufficient liquidity for their trading pairs. |
| Speed | Fast transactions. | Depends on the blockchain chosen. |
| Security | More vulnerable to cyberattacks due to their centralized nature. | Decentralized trading environments make it harder for attackers to compromise user assets. |
Fees |
Often charge trading fees that can range based on trading volume, order type, and market maker/taker status. | Gas fees, platform fees. |
| Examples | Binance, Kraken, Coinbase | Raydium, Sushiswap, Uniswap. |
The Growing Importance Of Cross-Chain Swap Technology In DEXs
In the traditional scenario, blockchain networks operate in isolation alongside each other. This siloed approach hinders the free flow of assets, data and value between different blockchains.
Cross-chain swaps became the answer, as the technology enables the direct exchange of assets between different blockchain networks, leading to a more integrated Web3 space.
How Cross-Chain Swap DEXs Changing Crypto Asset Trading
Cross-chain DEXs rely on innovative cross-chain communication protocols that allow the source and destination chains to communicate, enabling users to exchange assets across different blockchain networks.
Facilitating interoperability between different blockchain networks ensures traders have access to a larger pool of assets, leading to increased capital efficiency and improved liquidity conditions.
Uniswap, GravityDEX, THORSwap, and Polkadex are some examples of cross-chain swap DEX protocols that have become well-known in the DeFi community in recent times.
Note, however, that while the interoperability feature makes decentralized exchangers more versatile, it may also add a certain level of complexity to building cross-chain DEXs compared to typical DEX platforms.
Compliance Challenges In The DEX Space
Although decentralized exchanges present numerous advantages, they also pose substantial regulatory and compliance issues. Anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures have been touted among the most significant regulatory challenges DEXs face.
AML Concerns
The use of DEXs that operate without a centralized authority often causes challenges for anti-money laundering compliance efforts in cryptocurrencies.
The peer-to-peer nature of DEXs and the lack of traditional control provided by CEXs can make it harder to trace parties involved in suspicious transactions, potentially facilitating money laundering.
Additionally, the inherently anonymous nature of transactions on most DEXs makes it challenging to employ robust transaction monitoring systems that traditional financial institutions always use to identify suspicious patterns and flag potentially fraudulent activities.
On top of that, since DEXs operate on a global scale, the responsibility for AML regulation adherence is dispersed across multiple countries, each with its own AML regulations and enforcement mechanisms. This makes it complicated for DEXs to enforce AML standards.
KYC Concerns
Currently, most decentralized exchanges are not bound by KYC regulations.
Since users don’t need to verify their identity or the origin of their funds when they sign up for an account on a decentralized exchange, it’s much easier for DEXs to become a source of illicit activities like money laundering and terrorist financing compared to CEXs.
Therefore, many industry observers assume that it’s just a matter of time before DEXs find themselves subject to KYC requirements.
On the other hand, there are those who still believe that DEXs won’t forfeit user anonymity. After all, much of the appeal of decentralized exchanges is that traders are anonymous.
How To Tackle AML And KYC Challenges?
Addressing AML and KYC concerns is crucial for DEXs to reduce legal risks, build customer trust, and reduce the misconception that DEXs are only for black horses.
Several strategies that can be considered:
- Decentralized KYC Solutions. Biometric verification processes or virtual identity verification services could be the key to striking the right balance between regulatory obligations and the core values of decentralization.
- Collaboration With Regulatory Bodies on developing guidelines that help reach a middle ground — ensuring adherence without sacrificing decentralization.
- The Risk-Based Approach where DEXs evaluate the likelihood and potential consequences of money laundering risks specific to their operations. Based on this assessment, they develop and implement controls and mitigation strategies for reducing risks, tailored to the identified threats.
DEX Liquidity Pools: The Road Ahead
Decentralized exchanges have made good progress since their inception and are finally having their moment.
Strict regulatory pressures on CEXs are increasingly pushing traders towards decentralized alternatives that are less affected by these regulations.
Moreover, with the growth of decentralized finance, estimated to reach 507.92 billion USD by 2028, the popularity of DEX platforms like Uniswap and Raydium will only continue to rise, gaining ground over CEXs.
The expansion of digital banking development services, advances in privacy technologies, Layer 2 solutions, and user experience improvements will also play a role in moving DEXs towards greater maturity, and, ultimately, broader acceptance and recognition in the financial ecosystem.
Elinext — Your Trusted Technology Partner For Blockchain-Based Software Development
Elinext is a full-cycle financial software development company making success stories for over 27 years.
Whether it is creating currency exchange platforms, crypto-wallets, smart contracts, or blockchain networks, we are no strangers to heavy lifting.
To provide you with the evidence that Elinext is a team of experts with real-world experience delivering end-to-end blockchain services, we are sharing with you some key highlights from one of our recent, awe-inspiring projects, a Blockchain Solution for a Metals Trading Business.
Our Client chose us to build an intuitive and secure solution for managing private trade agreements.
Technician talent at Elinext have 8+ years of expertise in custom trading software development, so the Client’s expectations were fully met. Our engineers have managed to design a software product with a high level of client-server-blockchain architecture that relies on the Hyperledger Fabric blockchain network. Its permissioned nature ensures all deals, users, and warrants data are private and secured.
The features we added to the web app enable users to:
- explore warrants ownership history;
- manage deals, assign approvers, and add buyer organizations;
- confirm deals when agreement conditions are fulfilled;
- revisit the transaction’s history in case of controversial situations and more.
Learn more about our blockchain development solutions services and feel free to drop us a message if you think we can help out.