The continuously expanding use of mobile devices is leading to an increased number of applications designed to deliver financial and banking services. Despite the challenging situation in the global economy and the possibility of a recession, mobile apps continue to gain traction with consumers, while finance providers consider them as a significant component of their business strategies.
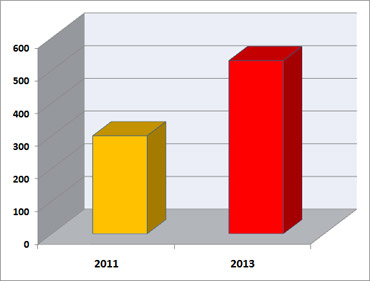
According to the recent report of Juniper Research, a company that renders mobile research, analysis, and forecasting services, mobile banking users worldwide from just over 300 million in 2011 will reach 530 million by 2013; whereby the highest penetration of users will have the developed markets of North America, Western Europe, as well as the Far East, and China. In some regions of the globe like the US, the usage of mobile banking apps already surpasses that of desktop-based ones.
What are the major benefits of mobile apps for finance organizations and banks? Obviously, the main advantage of mobile applications is that they offer all banks and finance companies an opportunity to improve customer acquisition and retention, whilst reducing operational costs. Thus, the expenditures on carrying out transactions get minimized, since many affairs are electronic and do not require human participation.
Research studies indicate that customers are getting comfortable with undertaking basic banking procedures on their mobile devices. Most common banking services performed on mobile phones have traditionally been SMS-based inquiries using text commands, that have typically been restricted to informational services such as transaction records, balance status, market information, and minor transactions related to account administration and settings. Nowadays sophistication of functionality is a trend in the evolution of mobile banking and finance applications.
The flexibility of modern mobile apps allows the performing of numerous transactions across various national and international banks. Moreover, in the near future financial institutions anticipate customer demand for smart apps designed for mobile platforms, such as iPhones, iPads, and Android devices. This is also confirmed by the fact that many consumers nowadays are seeking for reliable and effective ways to control and to increase their finances in uncertain economic times and conditions. In this situation, mobile applications from finance organizations can supply underserved clients with means to manage and leverage investment or business opportunities. For example, target clients can receive loans for business development via mobile phones.
Overall, various forecasts suggest a continuous popularity growth of mobile payment solutions, as well as the evolvement of contactless technologies, such as near field communication (NFC), that facilitate payments with the help of mobile wallets, enabling consumers simply to wave their phones near a POS-device in order to make a payment, rather than use plastic cards with magnetic stripes. Therefore, the future of banking and finance services is tightly coupled to mobile technologies and platforms. Private clients tend to use mobile apps as the primary information and transaction medium for their banking activities. However, even now some banks still have no apps to offer their clients.
Industries and Technology Areas:
Industries: banking, finance, mobile banking, brokerage, insurance, investment, credit unions, trust companies, mortgage loan companies, pension funds
Technology Areas: mobile applications development, smartphones, iPhone, iPad, iOS applications development, Android applications development, BlackBerry, Windows Mobile, tablet, PDA