A strong go to market strategy for technology products combines market research, customer segmentation, and value proposition development. In 2025, 74% of launches used digital channels and analytics for go to market execution. A SaaS startup’s GTM plan included influencer partnerships and targeted advertising, which resulted in a 50% increase in customer acquisition rates. Analytics show that data-driven GTM strategies reduce launch failures by 36% and improve early adoption, ensuring new products reach the right audiences effectively.
What is a Go-To-Market Strategy
When we are talking about tech companies, you should keep in mind, odds are nearly even for yours to make it to five years of existence. A go to market strategy for software products defines target users, value, channels, pricing, and launch.
CbInsights poll failed startups to get to know the reasons behind their failure. In more than 40% of the cases, it is the absence of market need to the product/service of that company.
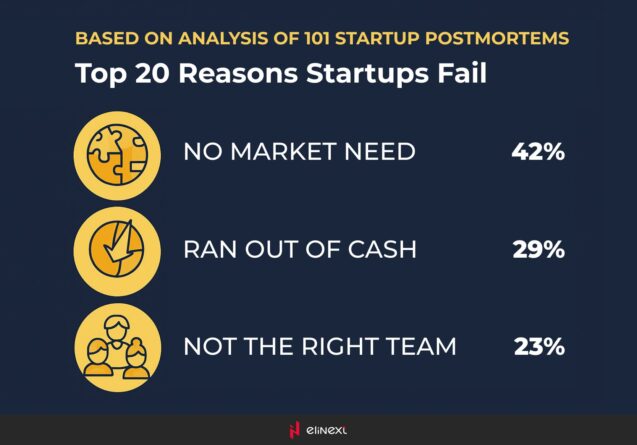 CbInsights poll failed startups to get to know the reasons behind their failure
CbInsights poll failed startups to get to know the reasons behind their failure
A go-to-market (GTM) strategy resembles a business plan, but of a wider scope and with extra factors.
In its essence, it is a tactical action plan with viable steps that are needed to be made in order to conquer a new market.
Gartner’s definition is the following:
“A go-to-market (GTM) strategy is a plan that details how an organization can engage with customers to convince them to buy their product or service and to gain a competitive advantage”.
This is more or less a complex version of the marketing plan with the scope of the core product (service).
What are the Key Elements of Go-To-Market Strategy
A new product go to market strategy includes a clear value proposition, target audience definition, competitive analysis, pricing, and distribution plans. Elements of a go to market strategy also include sales promotion and marketing tactics. A software company’s GTM plan included webinars and free trials, which increased signups by 40%. Analytics show that well-structured GTM strategies double customer engagement within the first 90 days.
Who: Your Target Audience
What: Your Products and/or Services
Why: Your Brand Positioning
Where: Your Target Markets
How: Your Marketing & Sales Plan
When: Timing

Get a tailored Go-To-Market strategy executed for your new product—positioning, pricing, channels, and KPIs.
Request a rapid audit and roadmap today.
How to Deliver GTM
An experienced entrepreneur is able to choose the pain point and message of his/her product, produce the content, ads, and apply a sales model for reaching the market.
With product confidence, shift to go to market execution: choose a large market and perfect the pain point, brand, messaging, content, ads, emails, and sales model needed to reach and convert that market.
To launch a product or service, craft a clear go to market strategy for software products: define the target audience, then do the hard work of engaging them to adopt your offering.In general, an actionable GTM plan includes four phases (the classification could differ for different schools of thought):
- Planning
- Roadmapping
- Marketing Strategy Development
- Customer Relationship Establishment
First, it clarifies why you’re launching your product, who it’s for, this stage includes a lot of planning and research.
That helps you define a roadmap for your future product
Next comes the hard part: executing a go to market strategy for technology products to drive customer engagement through targeted marketing and sales activities.
The final stage of GTM strategy is in securing outstanding customer experience to the base you already possess (in theory)
As noted, there are alternative ways to build a strategy. Below is a description of two approaches, often supported by software product engineering services.
Hubspot’s author Stefan Groschupf advises the following steps on his way to building GTM strategy:
TechTarget identifies the following must-haves for building a GTM strategy. We won’t publish their complete strategy but will recount what they consider GTM must-haves.
Phases of Delivering GTM Strategy In Detail
Phase One: Planning
OK, you have your idea. It is time to do your homework. Prepare for the long research and distributing plans for every part of the operation.
It all starts with assessing feasibility. If you have the time, budget, and enthusiasm, proceed with a go to market strategy for software products by researching your potential audience’s pain points and validating demand.
Defining the problem your solution solves. Leverage business analysis solutions and ask:
- What is the core problem resolved by my potential product?
- How relevant is this problem on the market?
- Does my product offer the solution of the target market better than existing products?
Ideally, if your ideas feats the market, the pain points of the customer should be found. For defining the value of your product, a value matrix is often created. That also would help to send a message to the market in the future.
At the planning phase, you’d have to study the market and buyer persona. Here are the questions you should ask to build the buyer persona:
- Whose problem do your solutions solve?
- What are the core industries for my product?
- Which level of the company do you target?
- Are the potential users aware of the problem you’re solving?
- Does your product look like the best solution to their pain-point?
The last question opens yet another box of Pandora. Which is called the research of demand and feasibility of the project. Studying competitors is vital at this point.
Also, you should assess additional financial risks, connected with legalities, territorial restrictions, but only after you’ve figured your product has chances of living in the current market conditions.
Everything in planning and researching your product begins at this first stage. Seasoned business analysis is crucial to generate insights that shape your future product and define the elements of a go to market strategy.
Phase Two: Roadmapping
You create an outline for the product’s development pathways, aligned with a go to market strategy for software products to guide positioning, channels, and launch. This is a very individual and industry-dependent stage. There are plenty of solutions for roadmap building on the market.
Below is the screenshot for including new features to a product based on Aha! Software. Below is the screenshot for including new features to a product based on Aha! software.
The key question to ask when crafting a product roadmap—especially within a go to market strategy for technology products—is: which initiatives most effectively deliver user value and market impact now?
How will you develop and introduce a new offering to the market?
At this stage, your ideas receive the first material actionable plan.
We at Elinext have a professional approach for software product engineering that allows us to create high-quality software that competes on and excels in the market. If you have an idea for a product but stumbled upon any mentioned stage, contact us – we will figure out ways we could help you.
Phase Three: Marketing Strategy Development
Modern SaaS B2B marketing—even for enterprises—often relies on content, paid ads, and classic digital tactics, but a new product go to market strategy integrates these with positioning, ICP focus, and multi-channel activation for faster adoption.
We’d like to give you some examples of how this strategy could be built
Cisco had a communication plan for a learning game to put users in the shoes of a telecoms company leader. The case is pretty ancient and an overall strategy might not be relevant in today’s environment, but the company released a presentation that includes major details of their GTM strategy.
This Slideshare includes the strategy, tactics, and assets used by the company, including the efforts on social media.
Marketing plans tend to include the following:
- Lead generation
- Content + website
- Inbound/Outbound marketing
- PR strategy
One has to outline the buyer’s journey, develop pricing and distribution strategies and develop your messaging for creating a working marketing strategy.
Phase 4: Customer Relationships Establishment
To illustrate how a great relationship with customers should be established, we should explore large enterprises entering new markets.
A role model is Huawei entered India. They showed by example how to build connections between the company and their customers.
Firstly, they have built R&D and service centres – live facilities in India. They hired mostly local people to show their commitment to the market. They realized that India is the second biggest market in the world, so they constructed the second-largest research center here.
Their positioning was as an “aspirational product” and based their market strategy around that. The main focus was on establishing trustful manufacturer-customer relationships.
At this stage of the go to market strategy for technology products, you design the sales funnel and future customer support—foundations that are critical to sustained market presence and long-term product longevity.
Also, if your company is quite big, and it has plans to launch a new product, custom-built CRM might serve as a great help in establishing certain processes. It helps increase sales effectiveness, analyze sales, and other ways of customer interaction.
It might not be effective for a small startup, but almost a must-have for an enterprise-sized product company.
“A successful GTM strategy combines market analysis, product positioning and flexible implementation. For example, our clients use analytics-based campaigns and specialized software to enter new markets 50% faster. The right approach to GTM turns innovation into measurable business growth.”
— Elinext Product Expert
Conclusion
A successful go to market strategy for software products is based on understanding customer needs, digital marketing, and channel partnerships. A fintech company’s GTM plan that combined influencer campaigns and demo webinars doubled signups in three months. Analytics show that effective GTM implementation increases product adoption by 36% and reduces time to value. In 2025, using analytics, automation, and real-time feedback will ensure your software product reaches its target audience and drives sustainable growth.
FAQ
What is a Go-To-Market strategy for software products?
A go to market strategy for software products defines how you will launch and promote your new software. It covers, for example, market research, pricing, marketing messages, and sales channels to ensure your product reaches the right audience and is adopted quickly.
Why is a GTM strategy important for new product launches?
A GTM strategy reduces launch risks and accelerates growth. Identifying customer needs and choosing the right sales channels helps new products gain traction faster and avoids costly mistakes that can slow down adoption or lead to a failed launch.
What role does pricing play in a GTM strategy?
In a go to market strategy for technology products, pricing determines perceived value and competitiveness. Freemium pricing quickly attracts users, while tiered pricing maximizes revenue by effectively positioning your product in the marketplace.
How can businesses ensure successful execution of a GTM strategy?
Success comes from clear goals, data-driven decisions, and agile implementation. Companies that test messages, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and quickly adjust their actions during launch see higher adoption rates, lower costs, and better customer feedback than those that don’t.
How can companies measure the success of their GTM strategy?
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as customer acquisition, conversion rates, and revenue growth. The new app measures success by the number of signups and customer retention in the first 90 days. Analytics help refine the go to market strategy for future product launches.