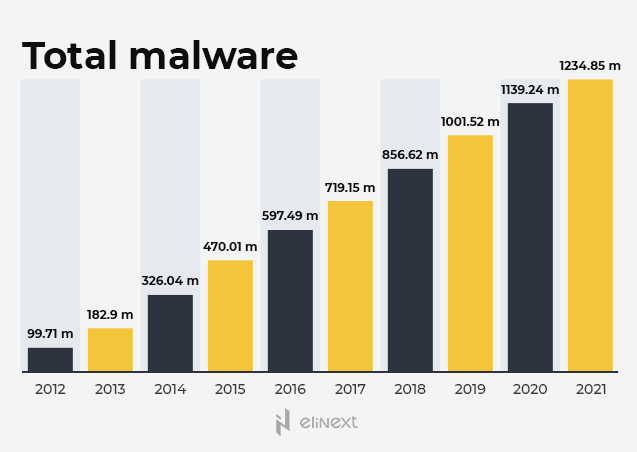
The digital revolution and the emergence of various top-notch solutions for different economic sectors stimulate business development and growth. At the same time, they raise the risk of cyberattacks that significantly increased worldwide in recent years. Deep Instinct revealed that malware grew by 358% in 2020. In this regard, the main question is how to protect your business and projects?
Hackers steal personal data to sell them and make a profit, while competitors hunt for your confidential information and intellectual property to harm your business. The research conducted by SafeAtLast shows that companies lose $133 thousand on average because of ransomware attacks. Moreover, these figures can even become higher because cybersecurity issues aggravated during the pandemic when employees from all over the world moved to remote work and attacks jumped by an impressive 600%. Let’s see how cybercriminals manage to break the systems and reach sensitive data.
Who Is Responsible for Data Breaches?
The most common causes of major cybersecurity violations can be divided into two categories: people and cyber hygiene. The human factor is related to the behavior of employees and how they interact with corporate systems. Cyber hygiene refers to the extent to which companies maintain and update their systems and software.
For example, the Office of the Australian Information Commissioner (OAIC) published a report indicating that 38% of all data leaks were caused by human errors. Attackers often take advantage of people’s carelessness, curiosity, greed, and anxiety.
For example, hackers sent out malicious emails about COVID-19-related topics. People received fake emails on behalf of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). They were offered to fill out a summary of recent cases of coronavirus among neighbors. For this purpose, they were asked to follow the link and enter their email login and password. As a result, criminals got their credentials.
Phishing has been and continues to be a huge business problem because employees often open unauthorized emails and install scumware on their computers. That’s why businesses must learn how to respond to the rise in psychological and phishing attacks. Security officers must inform employees who interact with systems and train them to recognize suspicious content and use strong passwords to protect their corporate accounts.
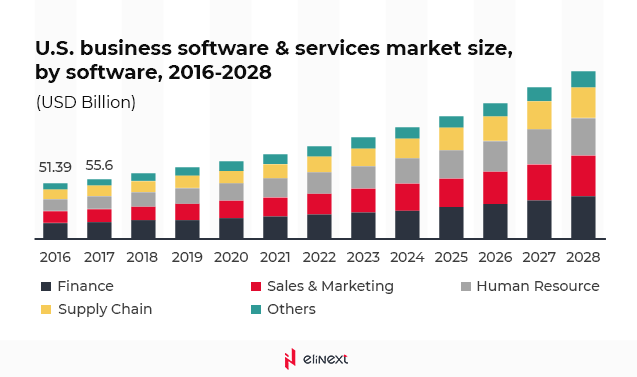
Custom software development companies should especially pay more attention to the protection of their projects. The eligraphics based on the Grand View Research data shows that the global software and services market value stood at almost $390 billion in 2020. It is predicted to grow by 11.3% by 2028.
Seeking to seize big investments and valuable information circulated in this sector, hackers come up with more and more sophisticated ways to break your security barriers. Taking into account the fact that software development companies often cooperate with freelancers and outsourced teams who work from home and use their own devices and networks, it’s vital for their business to protect their projects during and after the development stage.
Be On Guard of Your Confidential Information
There are two ways to protect private information: organizational data security measures and technical data security tools.
Organizational Data Security Measures
Every company (security officer or security department) must develop a set of organizational measures aimed at protecting confidential information. As a rule, it includes the following:
Technical Data Security Tools
The technical data security tools include the following software and hardware:
Security Testing
This testing strategy is aimed at checking software, data, and IT infrastructure for vulnerabilities and determining whether they are protected from hacker attacks. Security testing must be included in the software development life cycle (SDLC) from the first stages. The security testers usually perform the following tests:
- DDoS stress testing;
- Penetration testing;
- Vulnerability testing;
- Standard-compliant testing;
- Risk assessment;
- Ethical hacking;
- Security auditing.
These measures will allow you to reveal and fix weak points and be armed before the development stage. Gartner Insight expects companies to spend $170.4 billion on security by 2022.
Data Encryption
Encryption is the process of converting data into characters that cannot be read without knowing the rule (algorithm) by which they were created. Changing data using the selected algorithm is activated using a special key, which is also a certain set of characters. The longer the key, the more reliable it is. Without the key, the information will be a bunch of meaningless symbols.
Creating Strong Passwords
Each employee or project team member must come up with and use a strong, unique password. It must consist of numbers, characters, symbols, and letters so that hackers can’t crack it. The SafetyDetectives specialists analyzed more than 18 million passwords and revealed that the most predictable and hacked passwords were password in the US, 123456 in Germany, and qwerty in Russia. Criminals didn’t even have to try to guess for them.
It’s a very bad idea to use short passwords, too. For example, a computer spends milliseconds to crack a seven-digit password. If you find it difficult to create a reliable, long password, you can always use password managers that will help you protect your data.
Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication is a user verification method that includes an additional layer of security by requiring not one, but two identity facts at once. For authentication, people usually enter a username and password, which are easy to crack. For example, a login often matches a phone number and email address, while a password is easily guessable by answering security questions. In the case of two-factor authentication, another verification method is used. It can be scanning a fingerprint, identifying the user’s face, etc.
Antivirus Software
If a virus or malware enters your device, then all the above-mentioned measures will be useless. Hackers exploit viruses to transfer your private data and other confidential information to their servers. When choosing antivirus software, it’s important to pay attention to the ability to automatically update the antivirus databases as new viruses appear every day. AV-Test Institute detects more than 350k new pieces of malware per day.
Data Loss Prevention Solutions
While working on a project, the team and the customer constantly exchange various documents, files, passwords, logins, and other confidential information. Data Loss Preventions (DLP) solutions analyze incoming and outgoing data for confidentiality. When it is detected, the message transfer is immediately blocked. These instruments are currently gaining popularity. The DLP market size reached $1.31 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow to $3.75 billion by 2026, up 23.59%.
Data Backup and Recovery
Data backup is creating a copy of your files on another device or in the cloud in case the main device is lost or damaged. Using data backup and recovery solutions will allow your company not to find itself among 40-60% of businesses that filed for bankruptcy after data loss. The appropriate instruments and services will save you thousands of dollars because you won’t have to pay for downtime that reaches 16 days, according to the Coveware report. How much can your business lose if attackers break your systems?
Your Project is Launched: What Comes Next?
Signing a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) with your team will ensure data security after the development of your project. This agreement should define the rules for the transfer, disclosure, return, or destruction of confidential information after the completion of the project. Each party must clearly understand that it is responsible for the disclosure of any data. Of course, the NDA must be signed before starting work on the project. However, it must describe how to handle confidential information when the project is over.
Additionally, check whether your solution complies with the international security standards, such as ISO/IEC 27000 that defines the requirements to the information security management systems, GDPR that regulates personal data processing, and others. Also, always remember to observe the local laws and regulations.
Interested in security topics? Read more our articles.
A Brief Guide To Counter Cybersecurity Risks in IoT – Elinext